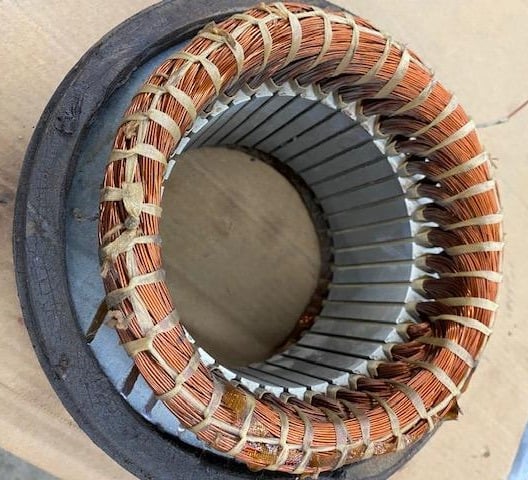
When you buy an electric motor, what is often unseen when handling it is the work that goes into helping extend its life by securing the end coils of windings. This process is called stator lacing. Tightly lacing the coils adds stability and helps protect the windings from vibration, which can cause fatigue and shorten a motor’s life. It also holds electronic, thermal, and other sensory devices in place during the dipping and baking process.
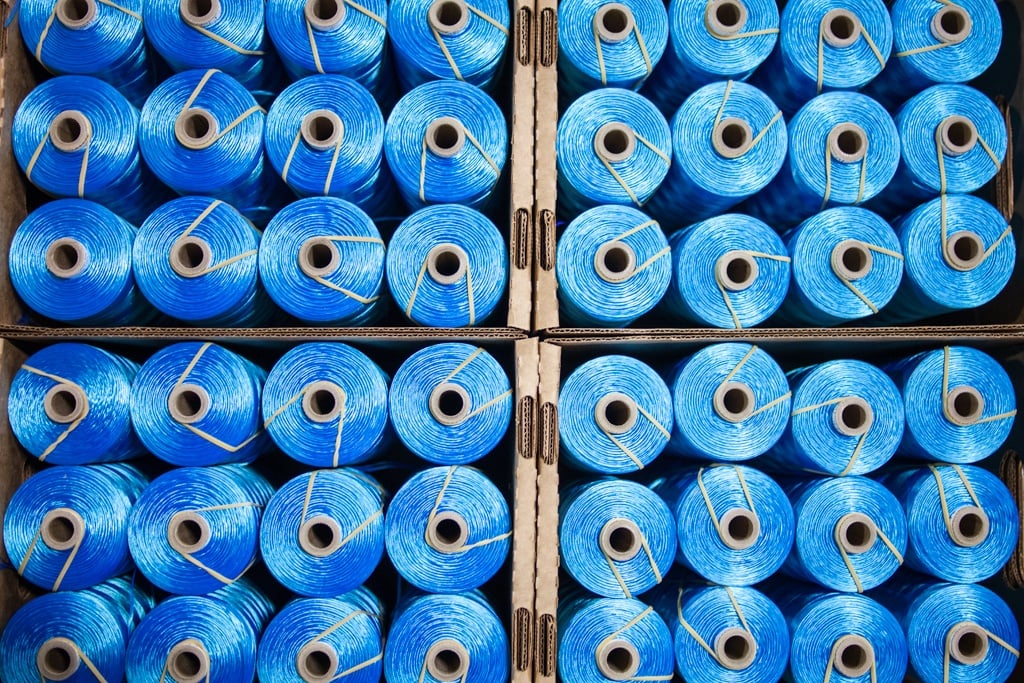
Service Thread’s round lacing cords are available in polyester, nylon, and para-aramid materials such as DuPont™ Kevlar® material. These are cabled constructions, typically three or sometimes four-ply, which offer a round cross-section. Round twisted sizes in nylon and polyester cords can range from number 138 to 690 (tex 135 to 700), offering minimum breaking strengths in the range of 18 to 100 pounds.
However, most common round twisted sizes are number 346 (tex 350), number 415 (tex 400), number 554 (tex 600), and number 690 (tex 700), which offer minimum breaking strengths in the range of 45 to 100 pounds. Round twisted lacing cords number 138 to 690 (tex 135 to 700) will have a diameter between about .01 to .05 inches, while the diameter of most common lacing cords will be .035 inches plus or minus about 15%.
Flat number 554 (tex 600) nylon lacing tape is also a popular choice. Being wider than round twisted thread, it will spread the stress over the coil surface during winding and tying rather than having it located at a small radius. Flat tape also offers increased grip due to its larger surface area.
Round thread can be laced evenly from large supply packages of more than or equal to 10 pounds. Flat constructions are typically rolled to prevent any twisting of the tape. Round twisted lacing cords are much preferred over cable ties, which turn brittle over time through oxidation and break and leave sharp edges which can cut installers’ hands when reaching into confined spaces.
Lacing cords may have some physical requirements, depending on the motor design and coil assembly.
- By Service Thread
- 06/29/20
- 0 Comments
- By Dane Hatcher
- 06/22/20
- 0 Comments
Are you using the right industrial sewing machine? Things to consider when looking to purchase a new machine include stitch type, thread thickness, sewing material thickness, material density, speed, parts availability, warranty, and special features or abilities.
Read more- By Dane Hatcher
- 05/28/20
- 0 Comments
Is your industrial sewing process affected by thread skips, breaks, and shedding? In our latest video tutorial, Service Thread Sewing Sales & Tech Support Manager, Dane Hatcher demonstrates how to avoid thread problems by properly adjusting your machine.
Read more- By Service Thread
- 05/19/20
- 2 Comments
Bonded thread size is communicated in various ways, mainly by ticket number and tex size. Although it’s easy to get caught up in the lingo and confuse the two, the ticket number and tex size are distinct characteristics of a bonded thread.
Read more- By Eric Shippee
- 05/07/20
- 0 Comments
Anyone who works with industrial fabrics knows DuPont™ Kevlar® has a reputation for being one of the world’s toughest fabrics. However, it’s sometimes criticized for being impossible to dye. This isn’t completely true.
Read more- By Dane Hatcher
- 04/15/20
- 0 Comments
When industrial sewing operations require high thread or yarn tensions, properly designed sewing threads and yarns are critical to continuous production flow. Bonded sewing thread and yarn tends to perform well for critical and challenging sewing conditions often faced by manufacturing companies. We’d like to provide some insight into how bonded thread affects tension in industrial sewing and manufacturing.
Read more- By Dane Hatcher
- 04/06/20
- 0 Comments
It’s important to evaluate whether you should be using a bonded or non-bonded thread in your industrial sewing process. For manufacturers, each type of industrial sewing thread or yarn has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, so let’s take a closer look at each option and which might be right for your application.
Read more- By Service Thread
- 03/23/20
- 0 Comments
When you’re sewing at high speeds, bonded thread prevents snags and breaks that cause production interruptions and create flaws in your products. In many applications, bonded sewing thread is almost always a superior choice.
Read moreNylon is a family of polymers, and all nylons share certain characteristics. However,there are some significant differences among types of nylon. Not all nylons are the same.
Read moreWhen you buy an electric motor, what is often unseen when handling it is the work that goes into helping extend its life by securing the end coils of windings. This process is called stator lacing. Tightly lacing the coils adds stability and helps protect the windings from vibration, which can cause fatigue and shorten a motor’s life. It also holds electronic, thermal, and other sensory devices in place during the dipping and baking process.
Service Thread’s round lacing cords are available in polyester, nylon, and para-aramid materials such as DuPont™ Kevlar® material. These are cabled constructions, typically three or sometimes four-ply, which offer a round cross-section. Round twisted sizes in nylon and polyester cords can range from number 138 to 690 (tex 135 to 700), offering minimum breaking strengths in the range of 18 to 100 pounds.
However, most common round twisted sizes are number 346 (tex 350), number 415 (tex 400), number 554 (tex 600), and number 690 (tex 700), which offer minimum breaking strengths in the range of 45 to 100 pounds. Round twisted lacing cords number 138 to 690 (tex 135 to 700) will have a diameter between about .01 to .05 inches, while the diameter of most common lacing cords will be .035 inches plus or minus about 15%.
Flat number 554 (tex 600) nylon lacing tape is also a popular choice. Being wider than round twisted thread, it will spread the stress over the coil surface during winding and tying rather than having it located at a small radius. Flat tape also offers increased grip due to its larger surface area.
Round thread can be laced evenly from large supply packages of more than or equal to 10 pounds. Flat constructions are typically rolled to prevent any twisting of the tape. Round twisted lacing cords are much preferred over cable ties, which turn brittle over time through oxidation and break and leave sharp edges which can cut installers’ hands when reaching into confined spaces.
Lacing cords may have some physical requirements, depending on the motor design and coil assembly.
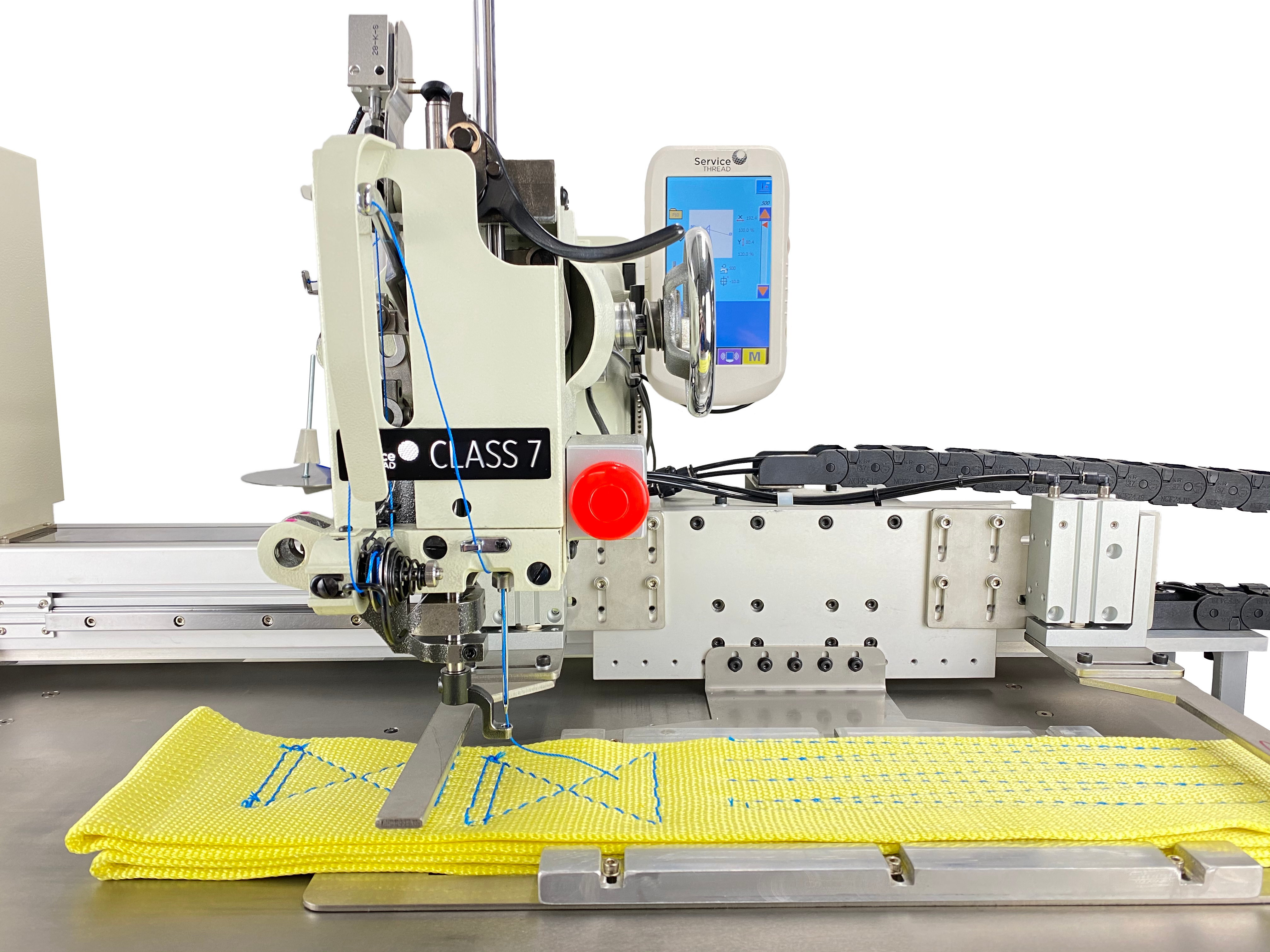
Choosing the Correct Industrial Sewing Machine for Your Application
- By Dane Hatcher
- 06/22/20
- 0 Comments
Are you using the right industrial sewing machine? Things to consider when looking to purchase a new machine include stitch type, thread thickness, sewing material thickness, material density, speed, parts availability, warranty, and special features or abilities.
Read moreTroubleshooting Series - Service Class 7 Troubleshooting Video Guide
- By Dane Hatcher
- 05/28/20
- 0 Comments
Is your industrial sewing process affected by thread skips, breaks, and shedding? In our latest video tutorial, Service Thread Sewing Sales & Tech Support Manager, Dane Hatcher demonstrates how to avoid thread problems by properly adjusting your machine.
Read moreWhat Is the Difference Between Ticket Size and Tex Size for Bonded Thread?
- By Service Thread
- 05/19/20
- 2 Comments
Bonded thread size is communicated in various ways, mainly by ticket number and tex size. Although it’s easy to get caught up in the lingo and confuse the two, the ticket number and tex size are distinct characteristics of a bonded thread.
Read moreCan Kevlar® Be Dyed?
- By Eric Shippee
- 05/07/20
- 0 Comments
Anyone who works with industrial fabrics knows DuPont™ Kevlar® has a reputation for being one of the world’s toughest fabrics. However, it’s sometimes criticized for being impossible to dye. This isn’t completely true.
Read moreWhat Effect Does Bonded Thread Have On Tensions in a Sewing Application?
- By Dane Hatcher
- 04/15/20
- 0 Comments
When industrial sewing operations require high thread or yarn tensions, properly designed sewing threads and yarns are critical to continuous production flow. Bonded sewing thread and yarn tends to perform well for critical and challenging sewing conditions often faced by manufacturing companies. We’d like to provide some insight into how bonded thread affects tension in industrial sewing and manufacturing.
Read moreIt’s important to evaluate whether you should be using a bonded or non-bonded thread in your industrial sewing process. For manufacturers, each type of industrial sewing thread or yarn has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, so let’s take a closer look at each option and which might be right for your application.
Read moreWhen you’re sewing at high speeds, bonded thread prevents snags and breaks that cause production interruptions and create flaws in your products. In many applications, bonded sewing thread is almost always a superior choice.
Read moreNylon is a family of polymers, and all nylons share certain characteristics. However,there are some significant differences among types of nylon. Not all nylons are the same.
Read more