Posts by Service Thread
- By Service Thread
- 12/11/19
- 0 Comments
- By Service Thread
- 12/03/19
- 0 Comments
The video above features untreated continuous multifilament polyester thread on the left, which burns vigorously once ignition temperature is reached, melts, emits black smoke and drips. Untreated aramid yarn on the right burns with difficulty because of high LOI. The flame extinguishes when the heat source is removed. Aramid does not melt but decomposes showing signs of thermal degradation.
Read more- By Service Thread
- 11/05/19
- 0 Comments
The video above features NeC 8/4 staple spun polyester. The untreated thread on the left burns vigorously once ignition temperature is reached, melts, emits black smoke and drips. The treated thread on the right melts and drips, however, resists combustion and flaming, therefore, smoke is greatly reduced, retardant has done its job.
Read more- By Service Thread
- 09/17/19
- 0 Comments
Ohm values vary for different industrial yarn and threads. Your choice depends on your specific application - do you need conductivity or static dissipation in your process or product?
Read more- By Service Thread
- 08/09/19
- 2 Comments
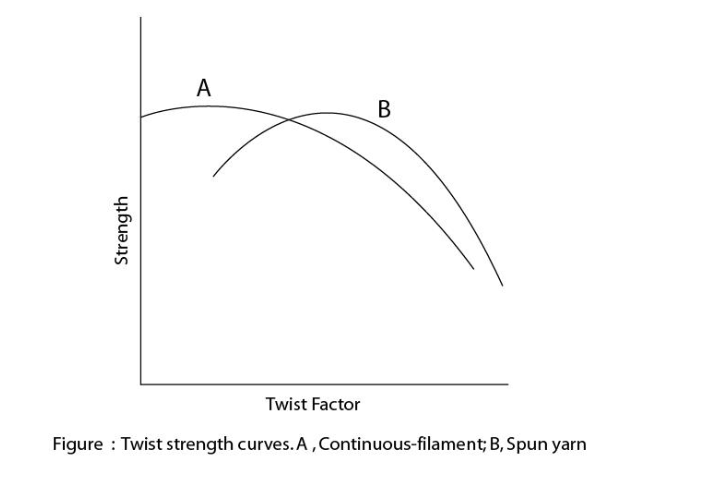
To understand twist contraction, think about a ship’s mooring rope. It’s a large, thick rope with thousands of yarns braided and twisted inside. Try to lift a section of the rope, and you’ll find it’s quite heavy.
Read more- By Service Thread
- 06/05/19
- 0 Comments
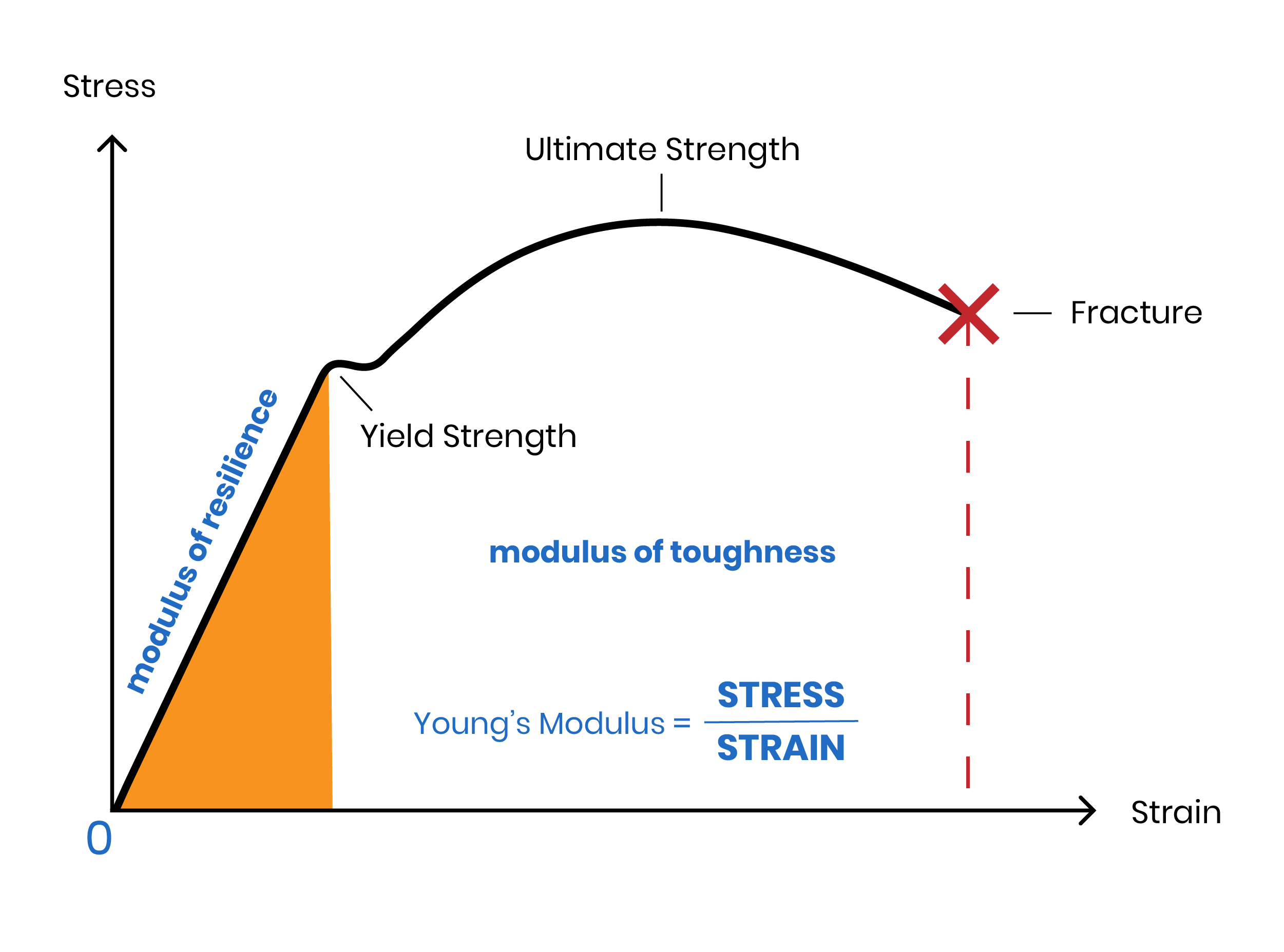
Every time you drive down the road and see suspended utility cables, you’re observing Young’s Modulus in action. The raised utility wires have a high modulus and are retaining their shape, even under the high pressures of aerial suspension and weather.
Read more- By Service Thread
- 07/17/17
- 0 Comments
- By Service Thread
- 09/25/15
- 4 Comments
Continuous filament polyester can be supplied in many forms but the most common for industrial applications are partially orientated yarn (POY) and fully orientated yarn (FOY).
Read more- By Service Thread
- 09/11/15
- 3 Comments
Modern nylon and polyester filament yarns share some similarities that may allow for cost reductions through materials engineering where polyester replaces nylon. However, there are some key differences to consider when designing an industrial sewing thread, hose reinforcement yarn, or textile binder or strength member. How are these fibers similar and how do they differ? The answers can be found in looking at the basic properties, and more importantly the end product application and environmental exposure to the fibers that will make all the difference in product success or failure,
Read moreService Thread

Recent Posts
The video above features untreated continuous multifilament polyester thread on the left, which burns vigorously once ignition temperature is reached, melts, emits black smoke and drips. Untreated aramid yarn on the right burns with difficulty because of high LOI. The flame extinguishes when the heat source is removed. Aramid does not melt but decomposes showing signs of thermal degradation.
Read moreThe video above features NeC 8/4 staple spun polyester. The untreated thread on the left burns vigorously once ignition temperature is reached, melts, emits black smoke and drips. The treated thread on the right melts and drips, however, resists combustion and flaming, therefore, smoke is greatly reduced, retardant has done its job.
Read moreUnderstanding Ohm Values in Conductive Yarns or Yarns for Static Dissipation
- By Service Thread
- 09/17/19
- 0 Comments
Ohm values vary for different industrial yarn and threads. Your choice depends on your specific application - do you need conductivity or static dissipation in your process or product?
Read moreTo understand twist contraction, think about a ship’s mooring rope. It’s a large, thick rope with thousands of yarns braided and twisted inside. Try to lift a section of the rope, and you’ll find it’s quite heavy.
Read moreWhat is Young’s Modulus?
- By Service Thread
- 06/05/19
- 0 Comments
Every time you drive down the road and see suspended utility cables, you’re observing Young’s Modulus in action. The raised utility wires have a high modulus and are retaining their shape, even under the high pressures of aerial suspension and weather.
Read moreContinuous filament polyester can be supplied in many forms but the most common for industrial applications are partially orientated yarn (POY) and fully orientated yarn (FOY).
Read moreMaterials Science for Industrial Threads and Yarns - Polyester and Nylon
- By Service Thread
- 09/11/15
- 3 Comments
Modern nylon and polyester filament yarns share some similarities that may allow for cost reductions through materials engineering where polyester replaces nylon. However, there are some key differences to consider when designing an industrial sewing thread, hose reinforcement yarn, or textile binder or strength member. How are these fibers similar and how do they differ? The answers can be found in looking at the basic properties, and more importantly the end product application and environmental exposure to the fibers that will make all the difference in product success or failure,
Read more