 PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) is a thermoplastic polymer with a very low coefficient of friction along with excellent chemical, temperature, and environmental resistant properties. Commonly known by its brand names of Teflon™ , Yeumiflon® , or Profilen® , PTFE can be manufactured as a specialty fiber or thread for a broad range of applications including filtration, outdoor fabrics, electrical cables, and protective garments.
PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) is a thermoplastic polymer with a very low coefficient of friction along with excellent chemical, temperature, and environmental resistant properties. Commonly known by its brand names of Teflon™ , Yeumiflon® , or Profilen® , PTFE can be manufactured as a specialty fiber or thread for a broad range of applications including filtration, outdoor fabrics, electrical cables, and protective garments.
Advantages
Virtually chemically inert – there are only a few chemicals that can affect PTFE fibers and only elementary alkali metals such as sodium can permanently damage the material.
100% UV resistance – PTFE fibers do not degrade in the presence of UV light unlike polyester and nylon. They will maintain their tensile properties indefinitely. This makes PTFE ideal for sewing outdoor fabrics.
Non flammable –PTFE has a very high LOI (>94%) and will not burn.
Low coefficient of friction – PTFE will repel most chemicals which makes it very effective as a filtration media. As a sewing thread, because of the very low friction, PTFE is basically self lubricating making it very easy to sew with.
Excellent thermal and electrical insulator – PTFE has a very high continuous service temperature of 500 deg F.
Appropriate for food and medical use – PTFE is approved by the FDA for use in food applications and in the medical field
Disadvantages
Low mechanical strength – Tenacity of PTFE fibers is typically between 2.5 and 4.0 gpd depending on the material type and color. This is approximately 1/3 of the nominal strength of a standard high tenacity polyester or nylon.
Higher cost – Due to the specialized process needed to make PTFE fibers, they typically cost more than most other fibers.
PTFE Compared to Polyester
Polyester is one of the most common low cost inherently UV resistant fibers available however unlike PTFE, polyester that is not UV treated looses strength after many years of extreme UV exposure. Below we have included a side by side comparison of PTFE vs. Polyester in approximately the same size sewing thread. Keep in mind, this is prior to any UV light exposure.
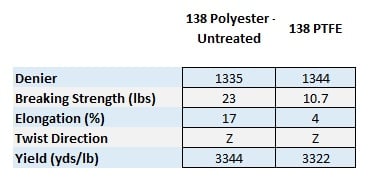
As you can see, polyester is twice as strong as PTFE prior to UV light exposure, the strength retention advantages of PTFE can only be seen over an extended period time. To give you an idea of how the two compare, we have included two graphs below that show the strength retention differences of untreated polyester vs PTFE under harsh UV conditions.
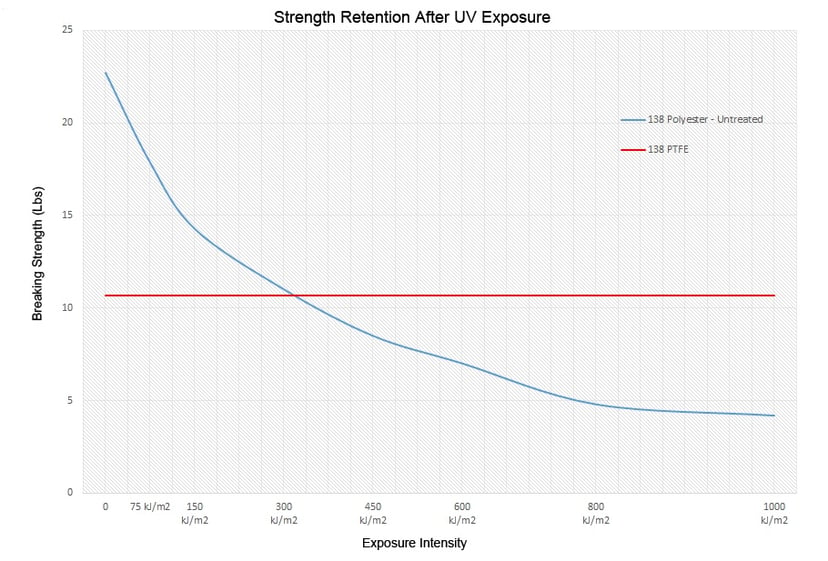
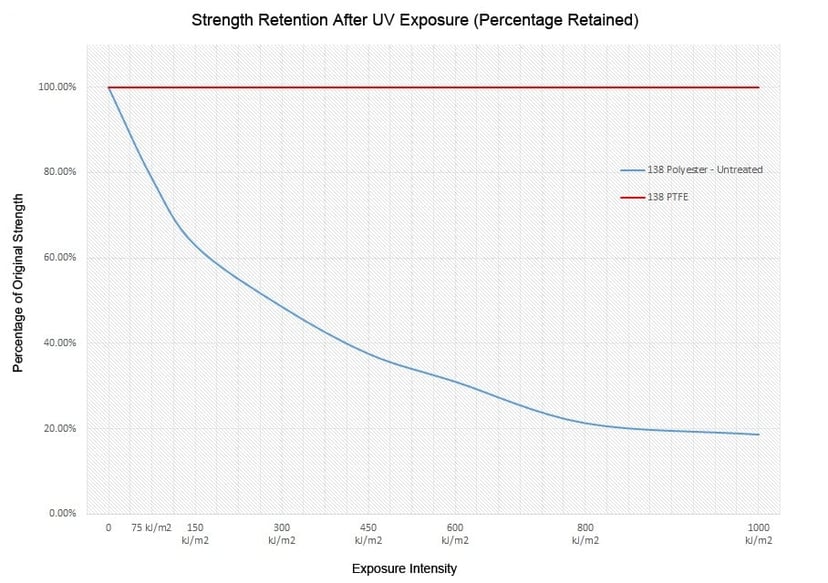
Depending on what you are looking to achieve, PTFE may or may not be the best fit for your application. At Service Thread we process PTFE, polyester, nylon, aramid and other high performance yarns and threads. If you need help determining the best yarn or thread specific to your application, please contact us, we would be happy to help!
Other Relevant Fiber Comparison Blogs:
-
The UV Resistance of Polypropylene and Polyester Explained
-
Polyester Vs Polypropylene for Industrial Thread and Yarn
-
Materials Science for Industrial Threads and Yarns - Polyester and Nylon



